New respirable crystalline silica regulations for General Industry and Maritime Industry employers in the United States went into effect June 23, 2018.
The new OSHA compliance standards for monitoring and protecting workers from respirable silica dust affect more than demolition and construction crews.
Maritime industry operators and a large section of companies involved in bulk handling must comply under the new standards.
This guide provides background and resources on the new OSHA enforcement and silica dust control strategy recommendations to help you avoid getting fined by federal inspectors.
What is respirable crystalline silica?
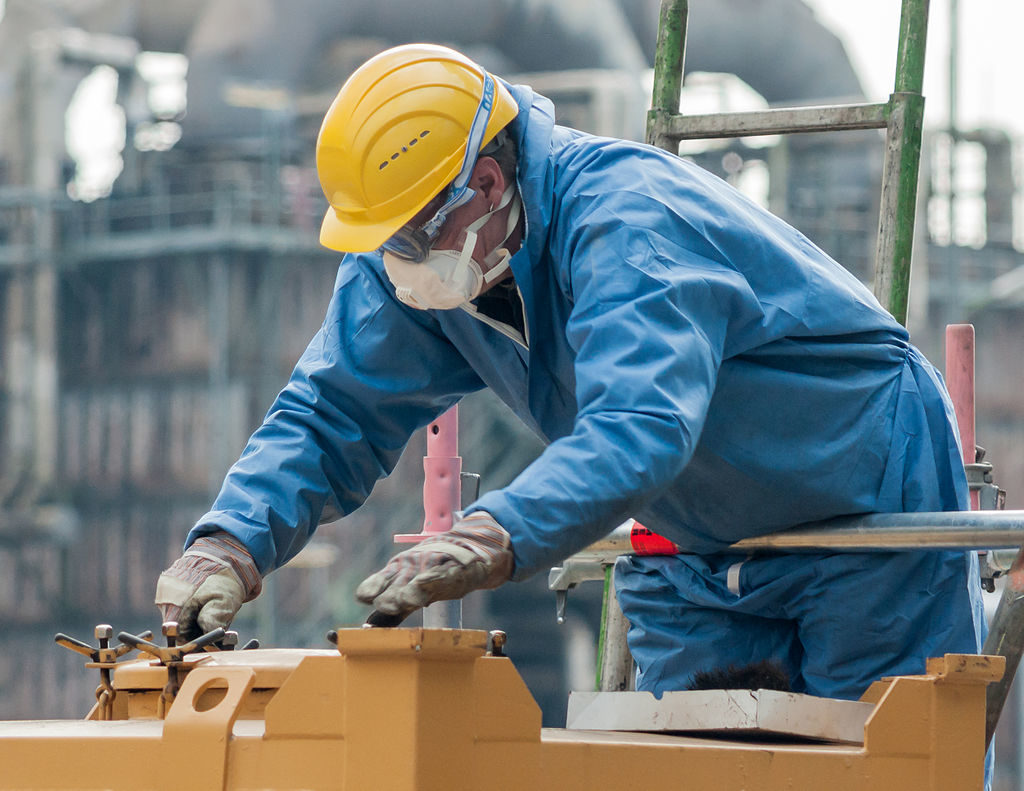

An estimated 95% of silicon dioxide produced is consumed in the construction industry. Silica is the main ingredient in sand and is found most commonly in quartz. It is contained in cement and steel slag products, and ceramic materials and it is used in sand casting for metals.
If materials containing silica are fractured or abraded, a respirable dust is emitted that if inhaled, can cause serious health complications including irreversible lung damage in some cases.
Federal authorities are serious about protecting you and your employees from silica inhalation, and experts believe OSHA regulators are preparing for a busy season enforcing the new codes.
2. Is my business affected by the new OSHA respirable silica exposure standards?

The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is directed by the U.S. Department of Labor.
Most likely. OSHA estimates that as many as 2.3 million workers in the construction and manufacturing industries will be affected by the new rule.
OSHA has expanded its enforcement standards to include a broad category of General Industry and Maritime employers, in addition to a variety of specific construction methods laid out in OSHA’s TABLE 1.
Hydraulic fracturing and abrasive blasting generally result in the highest levels of silica exposure. Under the new regulations, any company where silica dust is present – milling operators, scrap yards, paving mills, glass manufacturing companies, dry bulk handlers transport operators, and shipyard employers – can be now be fined.
Click here to view all of HKD Blue’s fugitive dust control solutions.
Understanding the new silica regulations is especially important for General Contractors unfamiliar with the regulations and for small subcontractors who may not be aware of the scope of the OSHA regulation changes.
Complete information on how to prepare for the new guidelines can be found here.
3. What should I do get OSHA compliant for the new silica standards?
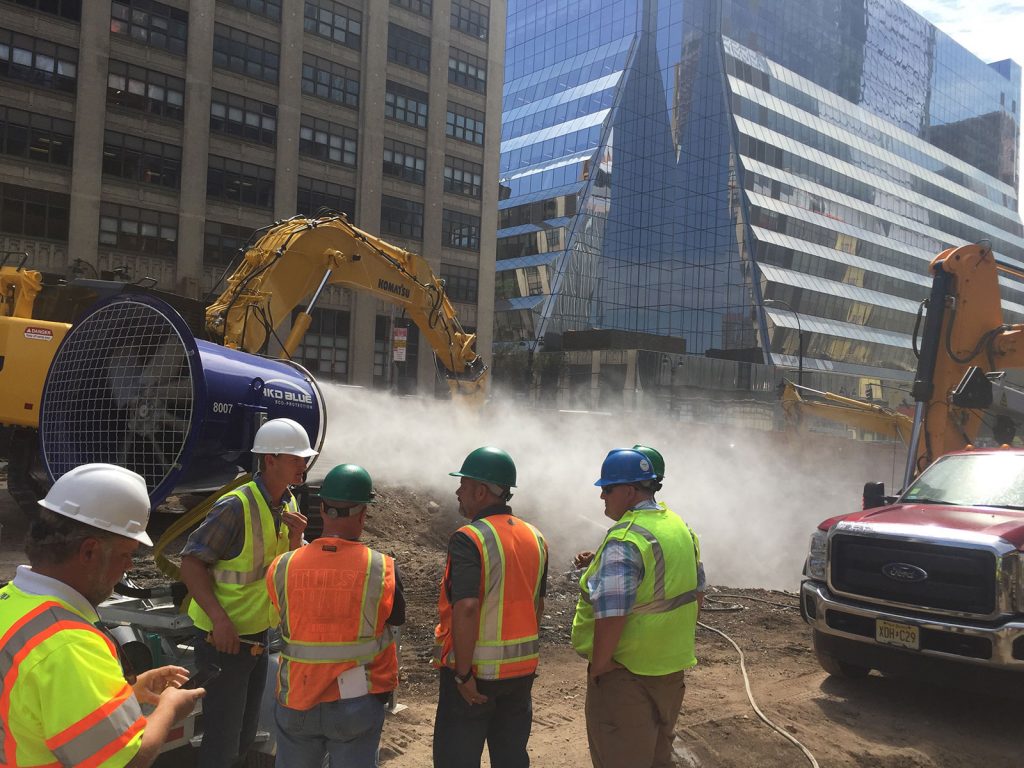

Start by assessing your individual employee’s silica exposure and create a list of all the potential silica emitting actions on your site:
crushing, sawing, manufacturing, transporting, bulk loading and unloading using machinery and infrastructure that crushes, abrades, demolishes, or facilitates bulk material handling.
Once silica exposure is identified, you must monitor the air for respirable crystalline silica levels.
What is the minimum activity level for silica exposure?
“25 µg/m3 (micrograms of silica per cubic meter of air), averaged over an 8-hour day”*
What is the minimum permissible exposure limit for silica?
“(PEL) of 50 µg/m3, averaged over an 8-hour day;”*
*Source: OSHA
4. Do I need atomized mist suppression machines under the new OSHA respirable crystalline silica standards?
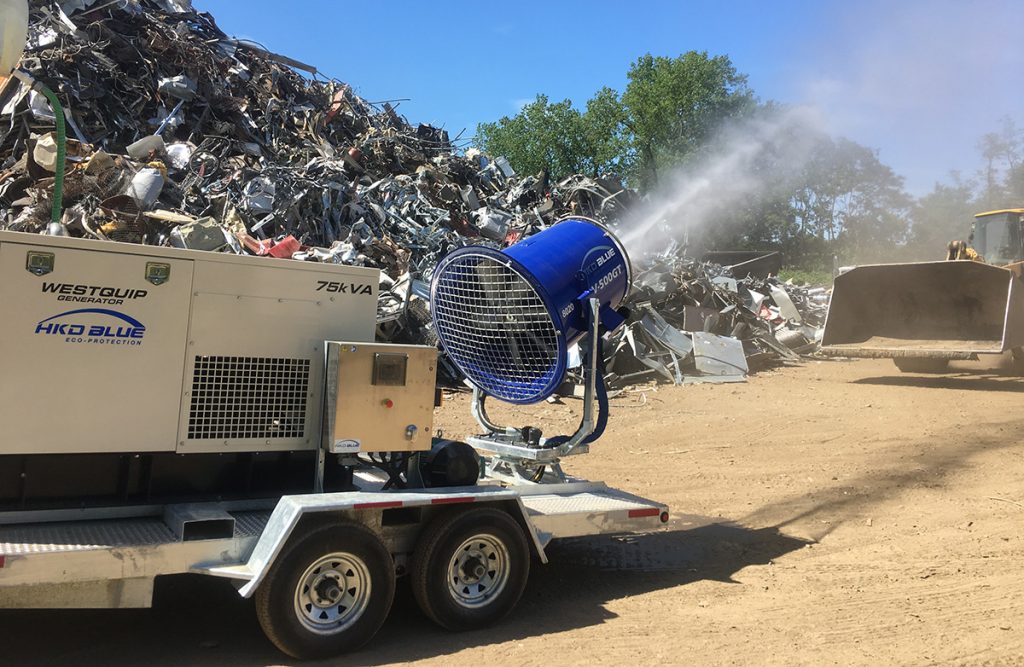

Your compliance actions depend on your industry. At a minimum, you will need to document your crystalline silica exposure assessment and make it available for OSHA inspectors upon inspection.
Tell us about your next construction job, demolition site, or bulk material port and we will send you a free Dust Control Compliance Strategy.
Use our strategy to help you create your written Exposure Control Plan that you must have in order to be compliant under the new OSHA regulations.
5. How much can you be fined under the new OSHA crystalline silica standards?
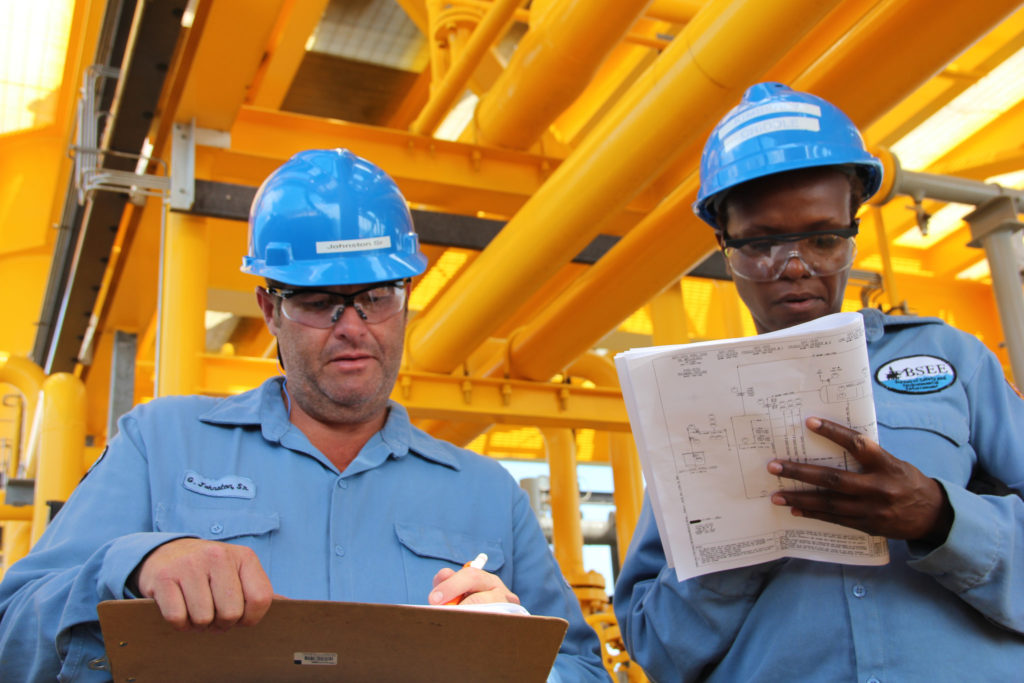

Federal inspectors on an unannounced inspection in New Orleans (Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement).
Bloomberg BNA reported recently that OSHA has already issued hundreds of citations in 2018 and that number is expected to increase throughout the peak of the 2018 construction season.
The maximum individual fine for a silica exposure violation is $12,675 but, you could wind up paying much more. OSHA says multiple violations in different areas of your site can result in multiple fines.
Repeated or willful violations of OSHA’s silica rules could land you up to a $126,749 fine that might compound daily.
6. How will HKD Blues atomized mist suppression machines work at your site or terminal?
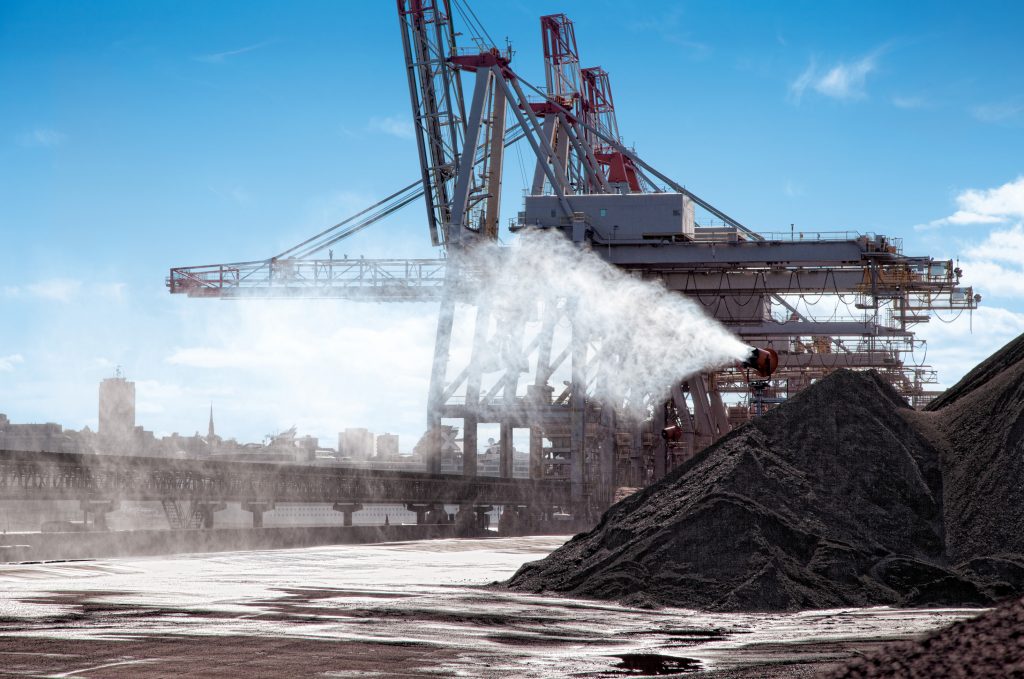

HKD Blue’s machines use water-atomized dust technology and can be adapted to all types of construction, marine, and general industry operations.
We have worked with demolition crews, and scrap yards across North America and have helped dry bulk operators move sensitive materials at major transloading terminals.
7. What are the requirements for General Industry or Maritime Employers under the new OSHA silica standards?
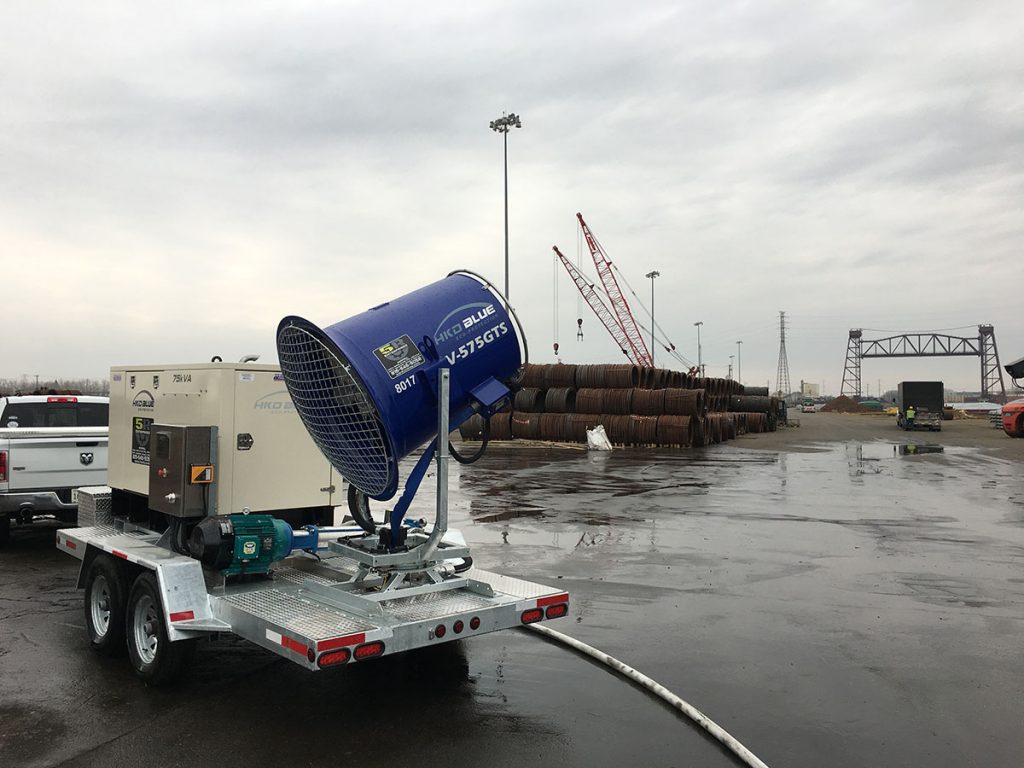

OSHA has specific instructions for maritime operators and general industry employers to help you prepare for the new regulations.
Read them here.
8. What types of construction and manufacturing companies need water-based dust control solutions?
Every site has its own unique challenges to controlling fugitive dust and complying with local and federal regulations.
Tell us about your site and we will send you a free Dust Control Compliance Strategy.
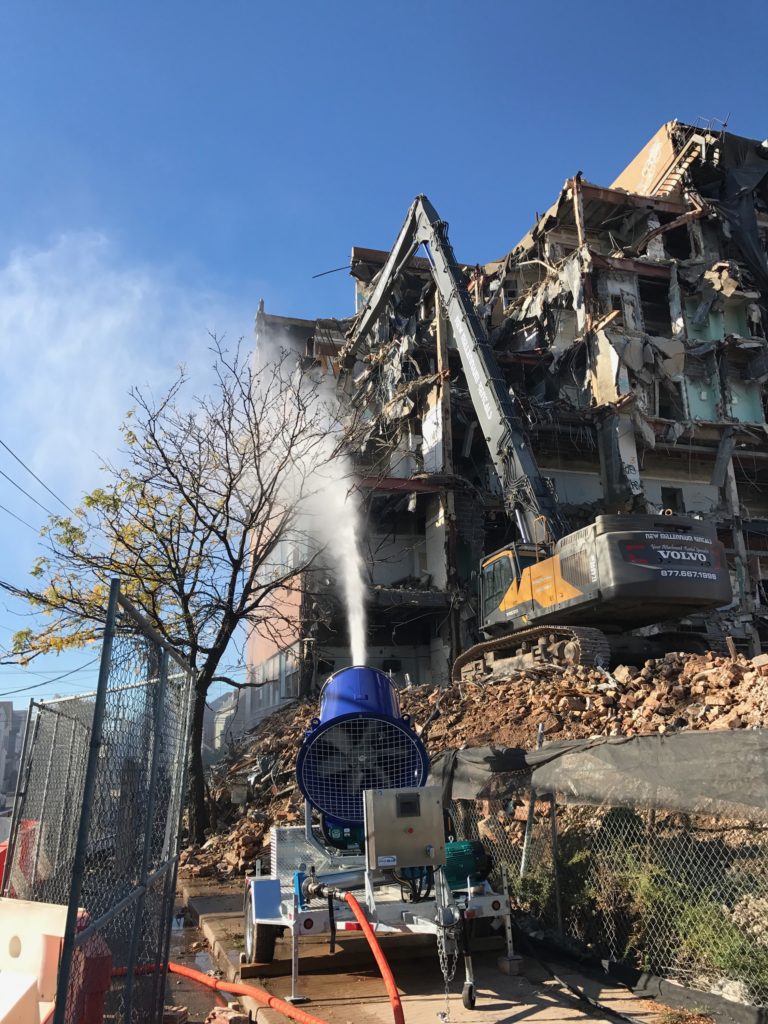

With a powerful 25 HP fan, dynamic V-Flow Central Nozzle HKD Blue’s machines provide effective dust control at the most sensitive job sites.